Our Processes
We use an integrated process where we combine the technical development process with a business development process. We call this combination Strikersoft's Business Value Model.
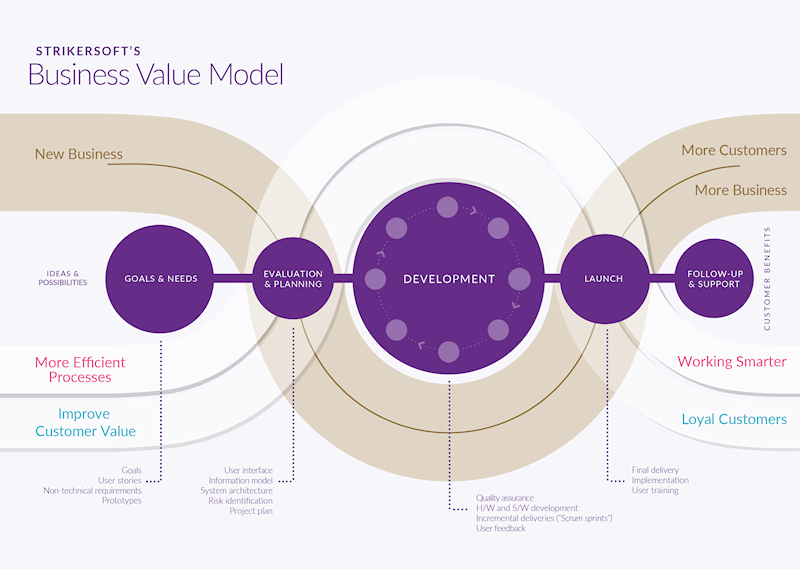
In addition to ensuring a technically high-quality product, delivered on-time and within budget, it also provides a solution that helps you work smarter, serve your customers better and also generate new sales for your business. This means that we focus more on your business goals than to formally follow the requirements.
Our customers often say that our process helps them to move from concept to customer value.
Business Value Model
Strikersofts combined technology and business process of product development is divided into five separate steps, where each part has clearly defined activities and deliverables. Throughout the process also the three business dimensions are assessed: efficient processes, increase customer value and new business.
1. Goals and needs
The work usually starts with a joint workshop. The major components of the agenda are
GOALS
- Specifies goals, both technical and business
- What problems is to be solved. Status of the problem today.
- More efficient processes – how to save cost in the operations
- Improve customer value - create additional benefits for the customers
- New business - find completely new revenue streams
USER STORIES
- Roles
- User stories by role, as straightforward as possible
3rd party systems
- Identification
- Interface
NON-TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS
- Non-functional requirements such as offline, platforms, performance requirements, UI language, CE requirements, etc.
- Allocation Plan, for example, onsite, cloud, etc.
- Design Requirements
PROTOTYPES
- Definition
- Clickable prototypes / wireframe
2. Evaluation & Planning
After the workshop the results are analysed in the evaluation and planning phase. Here the complete project is planned in detailed before the development is started.
USER INTERFACE
- Graphic design of the wireframe
INFORMATION MODEL
- Defines the relationship between the different objects
SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
- Describes the main parts of the system and their relationships
RISK IDENTIFICATION
- Identify, evaluate and produce an plan to minimize the risks
PROJECT PLAN
- A complete project plan is compiled for the next step in the process
3. Development
User stories and the non-technical requirements are broken down into tasks. The scope of a task is a person's work for a short period of time, in order to facilitate follow-up. Tasks are then grouped into Sprint. The result of the development of each Sprint is a working product with an increasingly enhanced functional content, delivered to the customer for testing and feedback.
QUALITY ASSURANCE
- Each Sprint is tested before delivery according to the requirement specifications
- Manual and automatic testing, e.g. automatic UI testing
H/W & S/W DEVELOPMENT
- Every developer receives his own task, which contains a number of well-defined development steps
INCREMENTAL DELIVERIES ("Scrum Sprints")
- Each Sprint is a working product with increasingly enhanced functional content
USER FEEDBACK
- Each Sprint is tested by users and the feedback goes directly into the next Sprint
FINAL TEST
- A final alpha test is done to verify the user stories and the non-technical requirements
Output at each delivery of the new Sprint:
- Change log, the changes compared with last Sprint
- Status report, how the project is doing in relation to the time schedule
- Test report, from the last test of Sprint
4. Launch
The product is ready for delivery to customers
FINAL DELIVERY
- Delivery of final Sprint with full functionality
- Interface to 3rd party systems switched to production systems
IMPLEMENTATION
- The customer puts the system in operation with real users
TRAINING
- Educate maintenance staff, train the trainers
5. Follow-up and Support
Is done based on a SLA (Service Level Agreement) where e.g. response time and monitoring schedules are specified. Maintenance of software contains e.g. software upgrade and new verification of compatibilities.
